
Joel P Joseph
In the previous article of this series, we had looked into Parkinson’s disease. In this article, we shall dwell upon Alzheimer’s disease.
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
One of the symptoms during the late stages of Alzheimer’s disease is the inability to remember familiar people, places or things.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease, affecting about 50 million people worldwide. The disease is named after Dr Alois Alzheimer, the first one to notice abnormal protein clumps in the brain of a woman who had died of this unusual mental illness. The disease mainly causes dementia –– the loss of thinking, remembering, and reasoning. Eventually, one finds it hard to conduct everyday tasks like wearing a shirt or tying their hair.
People above 60 years of age are at a higher risk of developing the disease. Such cases are called late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Sometimes, those aged 30-60 years can develop the disease as well. These cases are usually termed early-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
What happens to the neurons in Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease mainly affects cholinergic neurons –– the neurons that produce and release a chemical called acetylcholine. These neurons, present in the parts of the brain called the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex, are involved in forming and retrieving memories. As the disease progresses, these neurons stop working, lose connections with other neurons around them, and die. This loss of neurons causes the brain to shrink in size.
Characteristic features observed in neurons
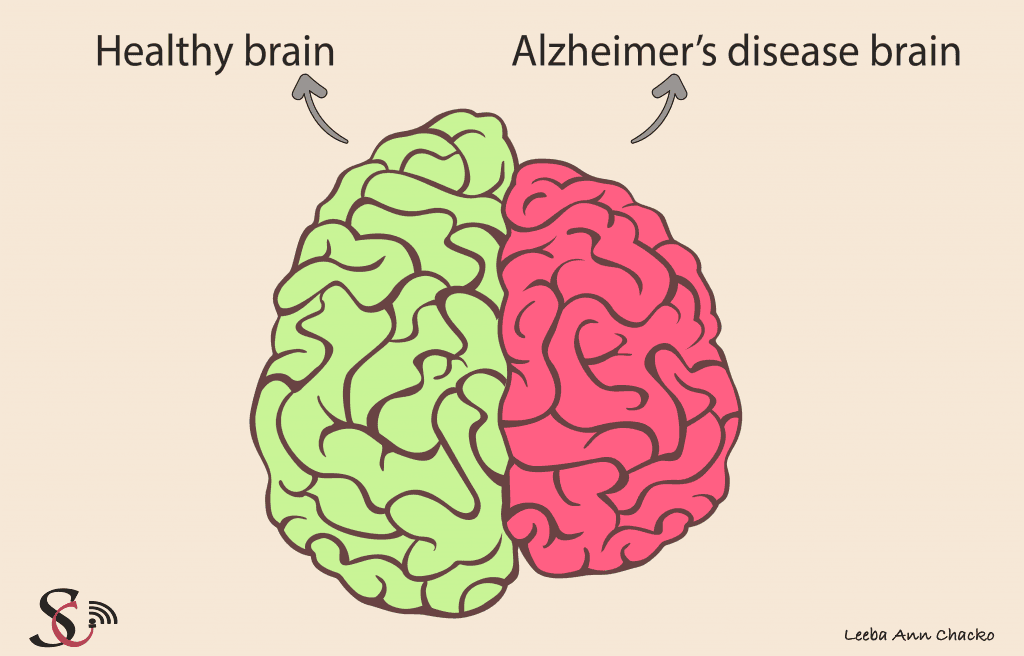
Patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease tend to have shrunken brains.
About a decade before the symptoms appear, several changes occur in the brain of an Alzheimer’s patient. Pieces of a protein called beta-amyloid form clumps in spaces between the neurons. These clumps are called amyloid plaques. Within the neurons, another protein called tau forms twisted fibres. These structures, called neurofibrillary tangles, are much like braided hair or twisted wires. These clumps of proteins eventually destroy the neurons.
Can Alzheimer’s disease be passed from parents to children?
It depends. It can either be hereditary or can be acquired by a person due to various factors.
The risk of developing the disease can be passed from parents to children in the form of some defects in the specific regions of the parents’ DNA. These distinct regions are called genes, and the defects are called mutations. Mutations in some genes, for example, the gene that codes for the amyloid protein, are passed on from parents to children. This increases the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease in children. Such a form of the disease is called familial Alzheimer’s disease.
On the other hand, the disease can also occur because of a combination of genetic, environmental, dietary, and lifestyle factors. In such cases, when the disease is not inherited, it is called sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.
Symptoms and stages
Some of the symptoms of patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
The first symptoms can vary from person to person. One of the earliest symptoms of this disease is problems with memory problems. However, some individuals show other symptoms that are not related to memory. These symptoms include difficulty in finding words, doing things that require thinking and reasoning, or wandering and getting lost.
The disease progresses through different stages.
Mild stage –– Individuals have memory loss and find it tough to do things that involve thinking. Sometimes, they wander and get lost, have trouble calculating change, face difficulty in repeating questions, or take longer to finish routine tasks.
Moderate stage –– Memory loss and difficulty in thinking and reasoning worsen. Patients are confused, unable to learn new things, have trouble recognizing family and friends, and doing things that involve multiple steps, e.g. getting dressed, brushing their hair, etc. Some may also experience hallucinations and delusions.
Severe stage –– Patients cannot do routine tasks on their own. They depend entirely on others and become bedridden towards the end.
Treatment
Treatment options for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
The current treatments for Alzheimer’s disease are not enough to cure it, but slow down the symptoms like memory loss, and manage the changes in behaviour. These drugs work by controlling different neurotransmitters –– chemicals that send messages from one neuron to another. Depending on the stage of the disease, different drugs that regulate different kinds of neurotransmitters are prescribed.
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the loss of neurons in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. This disease mainly affects the patient’s memory, thinking and reasoning. Symptoms include memory loss, difficulty in doing things that require reasoning, and locating a place. There is no cure for the disease, but the symptoms can be treated. Although scientists have an idea about how the disease is caused and how it progresses, they have been probing further to understand the disease better.
This article is a part of the series on Neurodegeneration. Find the rest of the articles from this series here.
Illustrator: Leeba Ann Chacko
Edited by: দেবদত্ত পাল। Debdutta Paul





